TM 5-6675-316-14
(3) When the ac voltage enters the control board, it is applied to C1 and R1
which provide a slight delay in the input voltage, which is applied to the timing
circuit composed of capacitor C2 and resistors R4, R3, R5, and external
potentiometer 1R1.
(Note that resistor R6 is not used in this application.)
(4) As the delayed ac voltage is applied across capacitor C2, the capacitor
begins to charge at a rate depending upon the setting of potentiometer 1R1. The
voltage across C2 also appears across rectifier CR1 and trigger diode CR2. When the
trigger diode reaches the breakover voltage of 43 ±5 V, it conducts to complete the
path across rectifier bridge CR1.
This forms a closed loop circuit through capaci-
tor C2, the primary of pulse transformer T1, and rectifier CR1, and current flows
until capacitor C2 is discharged.
The discharge time is very fast and a short
duration pulse is generated, shaped by capacitor C3.
(5) The pulse current flowing through the primary of pulse transformer T1
induces a voltage across the appropriate secondary which is applied through diode
CR3 or CR4 to the gates of SCR Q2 or Q1 respectively. When either SCR is triggered,
it allows the rest of the ac half-wave to pass to external grid lamp transformer 1T1
through pin B.
The SCR will continue to conduct until the ac half-wave reaches the
zero crossing point, at which time it turns off.
b. Clutch Control.
(1) X- and Y-axes manual motion controls are connected through electrically
operated clutches to chain drives.
Power to the clutches may be interrupted to
decouple chain drives and permit rapid movement of the optical mount in the X- and
Y-axes.
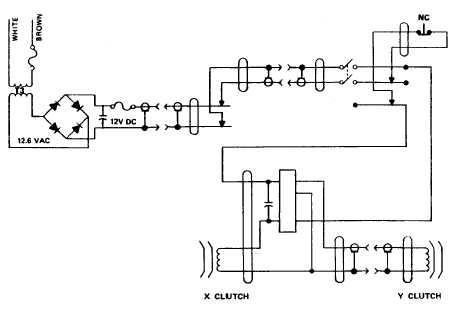
(2) Voltage, 120 V, 50/60 Hz, is stepped down to 12.6 V ac in the trans-
former, rectified in PCA A4 to 12 V dc.
Current passes through the quick-disconnect
and brushes to the quick-disconnect and clutch power switch.
The momentary switch
on the optical carriage is normally on except when depressed by the operator.
Twelve volts dc passes through the brushes to the series-connected clutches. Note
that the quick-disconnect separates the Y-axis clutch from the circuit.
4-7