TM 5-3610-257-14
d.
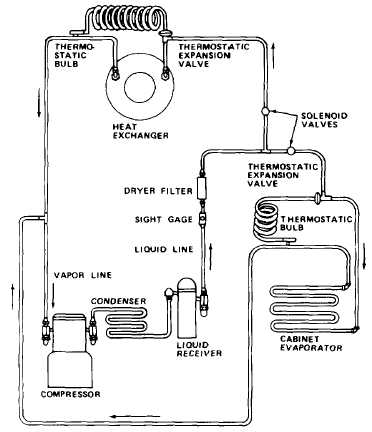
Sight gage. Indicates if freon lines are charged to capacity. With compressor running, a solid stream of liquid
refrigerant should be visible in the glass sight gage. If bubbles are present, the system is not fully charged.
e.
Dryer filter. Removes moisture from liquid refrigerant lines between liquid receiver and thermostatic expansion
valves.
f.
Solenoid valves. Controls liquid refrigerant flow to heat exchanger and cabinet evaporator coils.
9.
Thermostatic expansion valve. Thermostatically and pressure-regulated ball valve creates a pressure drop in
refrigerant flow. The pressure drop changes the refrigerant from liquid to gas, and heat is absorbed during the process.
h.
Cabinet evaporator. Located in the refrigeration cabinet. Its coils absorb heat from the cabinet. The evaporator
coils contain refrigerant which is vaporized by an expansion valve.
i.
Heat exchanger. Contains evaporator coils inside a solid housing which absorb heat from water pumped through
housing. The evaporator coils contain refrigerant which is vaporized by an expansion valve. The heat exchanger also
contains an immersion-type resistance heater to warm the water if temperature is too low.
5-3.2.
Recirculating System. Provides a temperature-controlled water bath to maintain a proper processing
temperature for processing solution trays located in the sink. It consists of a magnetic-drive, centrifugal pump which
recirculates water from the sink, through the heat exchanger, and back to the sink.
5-4