TM 5-6675-324-14
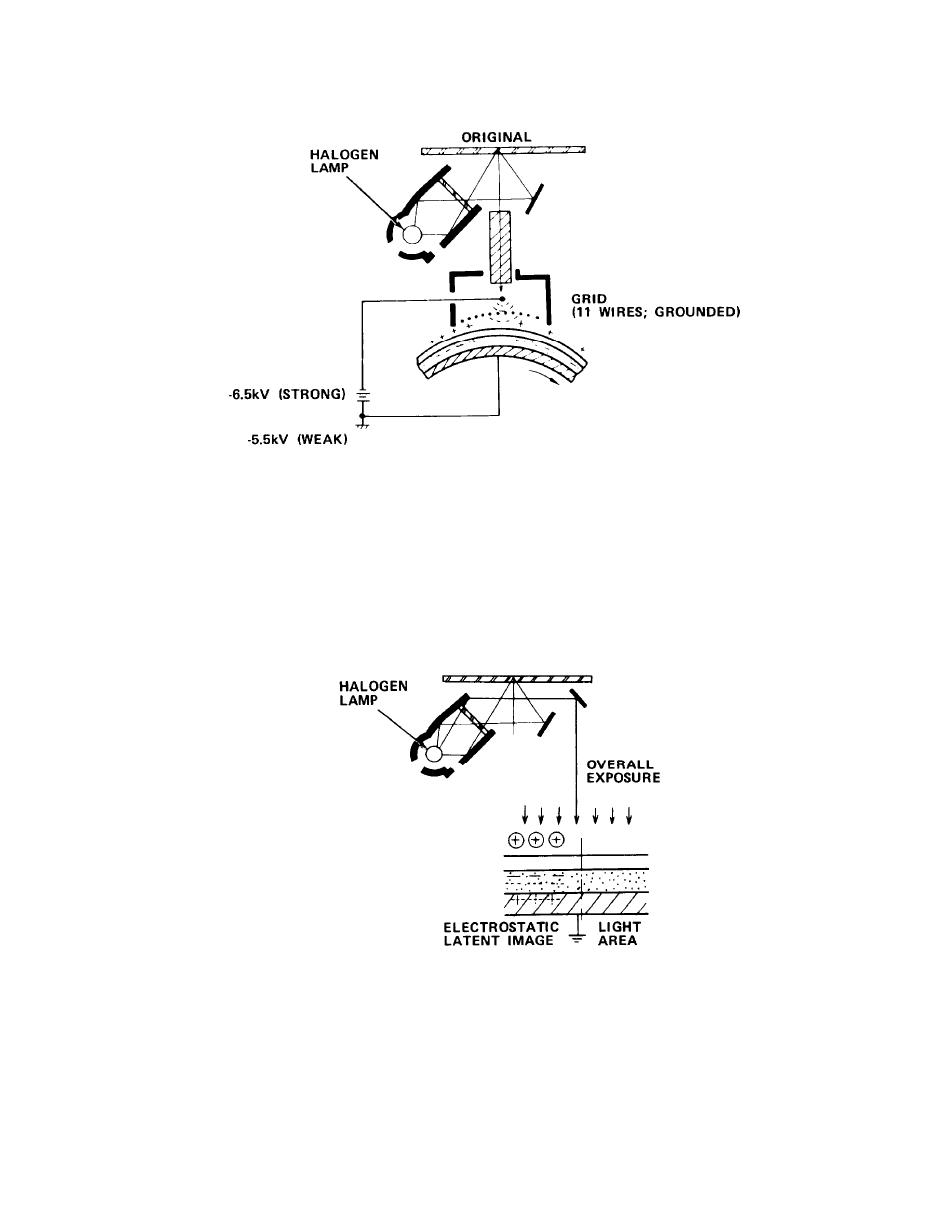
(3) Secondary corona image scanning exposure.
In this step, a narrow strip of the original is projected on the drum through the
lens array. The copyboard and drum surface move at the same speed, so the image is
spread around the drum. Where light strikes the drum, all positive charges are
removed and the resistivity of the CdS layer drops. In the dark areas, the CdS
layer resistivity remains high. The surface charge in both light and dark areas is
zero due to the balance attained by the positive charges and electrons. During the
scanning step, the corona is at -6.5 kV. This is reduced to -5.5 kV during the last
rotation so that the drum is not left with a negative charge.
(4) Overall exposure.
The overall exposure step reduces the resistivity of all areas of the CdS layer to
the same level. Trapped electrons are freed in the CdS layer. This intensifies the
effect of the surface" positive charges. The positive charges on the surface make up
the electrostatic latent image.
3-35

